Academic self-publishing is the act of publishing one’s work without the involvement of a traditional publishing house. This option has become increasingly popular in recent years, as it offers numerous benefits and advantages to academics. In addition to the benefits, there are also unique challenges that come with self-publishing which academics should consider.
In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of self-publishing in the academic world.
What Is Academic Self-Publishing?
Academic self-publishing involves the author taking care of all aspects of the publishing process, from writing and editing to formatting and distribution. This means that the author has full control over the content, design, and marketing of their work. Academic self-publishing also allows authors to bypass the gatekeeping role of traditional publishers, opening up the possibility for a wider variety of research to be shared.
Benefits of Self-Publishing in Academia
Here are the 5 benefits of self-publishing in the academic world.
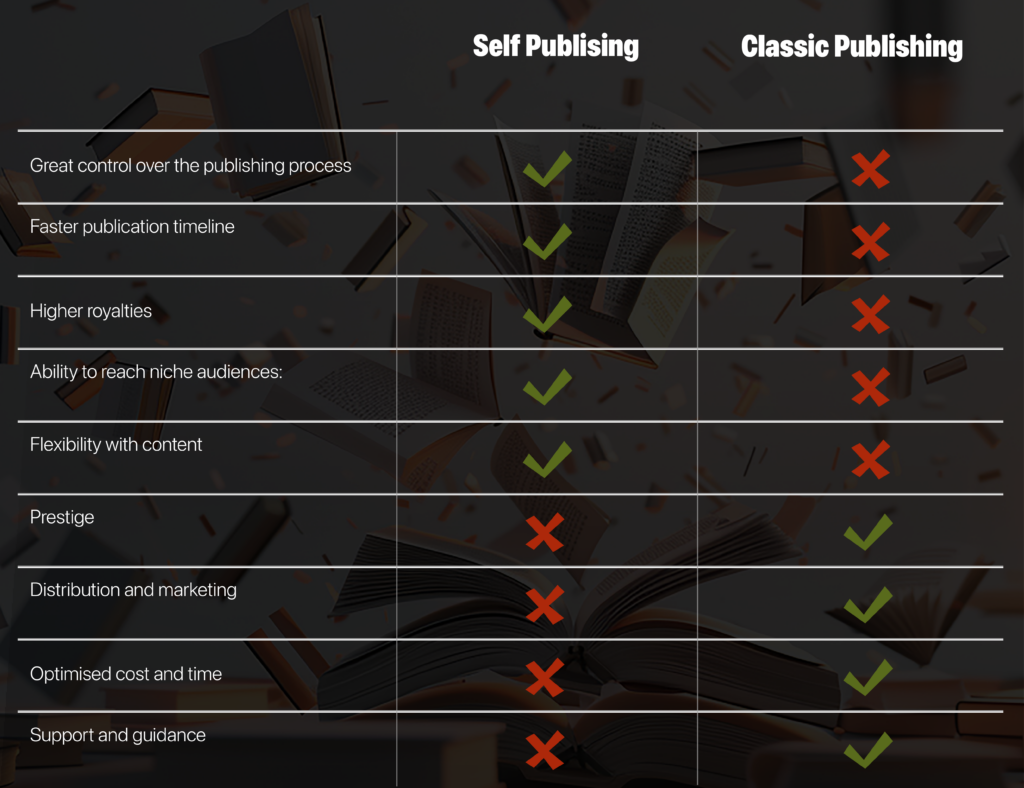
1. Greater control over the publishing process
With self-publishing, the author is in complete control of every aspect of the publishing process. This means they can choose the cover design, formatting, and distribution channels that best suit their needs and goals. Additionally, authors can make decisions about pricing and availability of their work, which can be particularly advantageous when trying to reach wider or international audiences.
2. Faster publication timeline
Traditional academic publishing can take years, with lengthy peer-review processes and waiting for publication dates. Self-publishing allows for a much quicker turnaround time, giving academics the ability to get their work out into the world sooner. For those who are working on timely subjects or whose research may quickly become outdated, this accelerated timeline can be a significant advantage.
3. Higher royalties
In traditional publishing, the author receives a percentage of the profits from their book sales. With self-publishing, the author keeps a larger percentage of the profits, often up to 70%. This can be especially beneficial for academic authors who may not have a large audience but still want to earn from their work. It also incentivizes authors to actively promote their work, as their financial gain is directly tied to their sales.
4. Ability to reach niche audiences:
Traditional publishing houses often have specific target audiences in mind, leaving some academic works without a publishing home. Self-publishing allows authors to reach niche audiences who may be interested in their specific topic or research.
This can be particularly valuable for those working in specialized fields or on topics that may not have broad commercial appeal but are nonetheless important within their disciplines.
5. Flexibility with content
Self-publishing gives authors more creative control the freedom to– include a wide range of content in their work, from images and graphs to footnotes and endnotes. Traditional publishing may limit the amount of content or require additional fees for certain types of content. Furthermore, self-publishing can accommodate unconventional formats and interdisciplinary approaches that might not fit the mold of traditional academic publications.
Disadvantages of Self-Publishing in Academia
Despite its benefits, self-publishing does have some potential drawbacks. These include:
1. Lack of prestige
In the academic world, traditional publishing is often seen as the more prestigious option. This may be due to the rigorous peer-review process and the perceived quality of the publisher. Self-published works may not hold the same level of credibility in the eyes of some academics, potentially impacting the author’s reputation and the work’s influence.
2. Limited distribution and marketing
Traditional publishing houses have established distribution and marketing channels, which can be difficult for self-published authors to replicate. This may result in limited reach and sales for self-published academic works. Additionally, without the support of a professional marketing team, self-published authors must often invest significant personal time into promoting their work, which can be a daunting task for those unfamiliar with marketing strategies.
3. Costs and time investment
While self-publishing can be more cost-effective in terms of royalties, it does require a significant investment of time and money on the part of the author. This includes hiring editors, cover designers, and marketing professionals, which can add up quickly. The financial risk is entirely on the author, and there are no guarantees of recouping the initial investment.
4. Lack of support and guidance
Traditional publishing houses often provide support and guidance throughout the publishing process, from editing to marketing. Self-published authors may not have access to this type of support, which can make the process more challenging. The responsibility for ensuring the quality and accuracy of the work rests solely on the author, which can be a heavy burden, particularly for those without extensive publishing experience.
Who Should Consider Self-Publishing in Academia?

Self-publishing is not for everyone, and it may not be the right choice for every academic. However, there are certain types of academics who may benefit from self-publishing, including:
Early-career academics
For early-career academics who are looking to establish themselves in their field, self-publishing can be a great way to get their work out into the world and build a following audience. This can be a strategic move for those who have struggled to attract the attention of traditional publishers or who want to demonstrate the impact of their research quickly.
Authors with niche topics
As mentioned earlier, self-publishing can be a great way to reach niche audiences that may not be served by traditional publishing houses. If you have a topic that may not have a large market, self-publishing can be a way to still get your work out there. It also provides an opportunity to connect directly with readers who are passionate about the subject matter.
Authors with a large following
Established academics with a large following and built-in audience may benefit from self-publishing, as they already have a built-in market for their work. These authors can leverage their existing platforms, such as social media or professional networks, to promote their books effectively without the need for traditional marketing channels.
Authors with time-sensitive content
For academics whose research is time-sensitive or on a current topic, self-publishing can be a way to get their work out quickly and capitalize on the timely nature of their research. In rapidly evolving fields, the ability to publish promptly can be a crucial factor in the relevance and impact of the work.
How to Self-Publish in Academia

If you have decided that self-publishing is the right choice for your academic work, here are some steps to get you started:
1. Research and plan
Before diving into self-publishing, it is important to do your research and plan accordingly. This includes understanding the self-publishing process, researching your target audience, and deciding on your goals for your work. You should also consider the competitive landscape and whether there are similar books on the market. Planning your approach to stand out and attract readers is essential.
2. Hire professionals
Self-publishing does not mean you have to do everything on your own. Consider hiring professionals, such as editors, cover designers, and marketing experts, to help you create a high-quality, marketable book. Investing in professional services can significantly improve the polish and appeal of your book, making it more likely to succeed in the competitive academic market.
3. Choose a platform
There are many self-publishing platforms available, each with its own pros and cons. Research and decide on a platform that best suits your needs and goals. Some platforms may offer better distribution options, while others might have more user-friendly interfaces or superior royalty terms. It’s important to choose a platform that aligns with your publishing objectives.
4. Format and design your book
Formatting and design are crucial for a professional-looking book. Consider hiring a professional to ensure your book is visually appealing and easy to read. Good design can enhance the readability of your work and make it more attractive to potential readers. Paying attention to details like typography, layout, and cover design can make a significant difference in how your book is perceived.
5. Market your book
Marketing is essential for any published work. Utilize social media, email marketing, and other channels to promote your book and reach your target audience. Building a marketing plan and setting aside a budget for promotional activities can help to increase the visibility of your book. Engaging with your academic community and participating in events can also help to raise awareness of your publication.
What are the self-publishing options?
There are several self-publishing options available for authors looking to publish their work. These options include:
1. Print-on-demand (POD) services:
Print-on-demandPOD services allow authors to upload their book files to a platform and have copies printed as orders are received. This eliminates the need for large print runs and reduces the upfront costs of publishing.
2. E-book publishing:

E-books are digital versions of books that can be read on devices such as e-readers, tablets, and smartphones. E-book publishing allows authors to reach a wider audience and can be done through platforms such as Amazon’s Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP) and Apple’s iBooks.
3. Self-publishing companies:
Several self-publishing companies offer a range of services, from basic formatting and cover design to marketing and distribution. These companies typically charge a fee for their services, but they can be a good option for authors who want professional help with the publishing process.
4. DIY publishing:
Some authors choose to handle all aspects of publishing themselves, from formatting and design to marketing and distribution. While this option can be time-consuming, it allows authors to have complete control over the publishing process.
5. Hybrid publishing:
Hybrid publishing is a combination of traditional publishing and self-publishing. With this option, authors work with a publisher who offers services such as editing, design, and distribution, but they retain more control over the process and may have to contribute financially to the publishing costs.
It’s important for authors to do their research and determine which self-publishing option is best for their needs and goals.
Each option has its benefits and drawbacks, and authors should consider factors such as cost, control, and distribution when making their decisions.
With careful planning and research, self-publishing can be a valuable option for academics looking to get their work out into the world.
Lambert Academic Publishing offers an easy and affordable publishing process that allows you to share your research with a global audience. With no publishing contract required and professional editing and formatting services included, publishing your academic work with us has never been easier. Plus, our worldwide distribution network ensures that your work will be seen by a wider audience.
Don’t let your research go unnoticed – publish your academic work with Lambert Academic Publishing today and take the first step towards sharing your findings with the world.
