
What Are the Three Types of Publishing?
The three main types of publishing are traditional publishing, self-publishing, and hybrid publishing. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges, and choosing the right one depends on your goals, budget, and level of creative control.
Traditional publishing involves working with established publishers who handle editing, design, and distribution but offer less creative control.
Self-publishing gives authors full control over the process, from production to marketing, but requires upfront investment and effort.
Hybrid publishing combines aspects of both, providing professional support for a fee while allowing authors more input and control.
Understanding these methods will empower you to make the best decision for your work.
Traditional Publishing, Self-Publishing and Hybrid Publishing Main Differences
| Publishing Model | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional |
– Professional editing & design – Wide distribution – No upfront costs |
– Lengthy timelines – Lower royalties – Limited creative control |
| Self-Publishing |
– Full creative freedom – Higher royalties – Faster time to market |
– All costs borne by the author – Marketing challenges – Limited physical distribution |
| Hybrid Publishing |
– Professional support – Faster process than traditional – Flexible control |
– High upfront costs – Varied quality of publishers – Complex royalty structures |
Traditional Publishing
What is traditional publishing?
Traditional publishing involves submitting a manuscript to a publishing house. If accepted, the publisher oversees the entire publishing process, including editing, design, and marketing, while the author focuses solely on writing.
Pros of Traditional Publishing
Professional Expertise: Offers access to skilled editors, designers, and marketing professionals who enhance your book’s quality and visibility.
Wider Distribution: Books are distributed through established channels, reaching bookstores, libraries, and online platforms worldwide.
No Upfront Costs: Publishers assume financial risks, covering production, distribution, and marketing expenses.
Cons of Traditional Publishing
Lengthy Process: Getting published can take years, from manuscript submission to distribution.
Less Creative Control: Publishers may alter content, cover designs, or marketing strategies without your input.
Lower Royalties: Authors typically earn 5%–15% book royalties, limiting earnings potential compared to other methods.
The latest data shows that revenue in the Books market worldwide is projected to reach US$91.98bn in 2024, meaning if you are ready to publish your research there’s a high chance people will buy it!
The latest data shows that revenue in the Books market worldwide is projected to reach US$91.98bn in 2024, meaning if you are ready to publish your research there’s a high chance people will buy it!
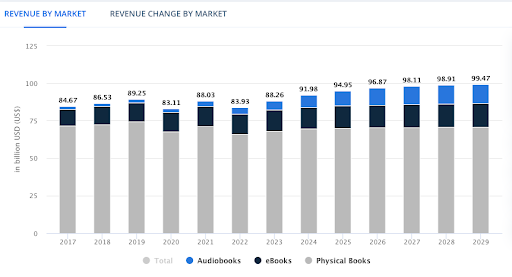
Source: Statista Market Insights
Self-Publishing
What is Self-Publishing?
Self-publishing allows authors to maintain complete control over their book’s publishing process, including editing, cover design, pricing, and marketing. Advances in technology and platforms like Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing have made this a popular choice.
Authors who choose this route can retain full ownership of their work and make decisions that align with their creative vision. Let’s discuss the main benefits of self-publishing.
Pros of Self-Publishing
- Creative Freedom: Authors retain full ownership and decision-making power over their work.
- Faster Time to Market: Books can be published quickly, often within weeks.
- Higher Royalties: Authors earn 35%–70% royalties per sale, significantly higher than traditional publishing.
Cons of Self-Publishing
- High Costs: Authors bear all expenses, including editing, cover design, and marketing.
- Limited Distribution: Access to physical bookstores and libraries can be challenging.
- Marketing Responsibility: Without professional support, authors must manage all marketing efforts.
Did You Know?
According to Statista, self-publishing accounted for over 1.67 million ISBN (International Standard Book Numbers)-registered books in the U.S. in 2018, demonstrating its growing popularity among authors.
Number of International Standard Book Numbers (ISBNs) assigned to self-published books in the United States from 2010 to 2018.
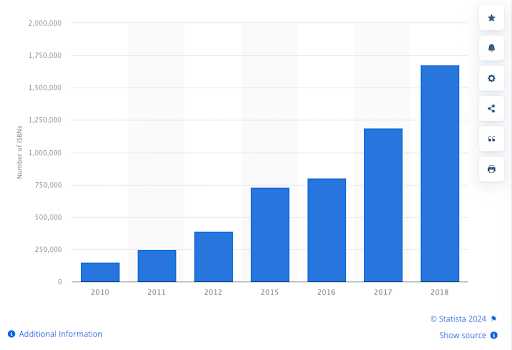
Source: Statista
Hybrid Publishing
Hybrid publishing combines elements of both traditional and self-publishing. In this model, authors pay for certain services while retaining some control over the publishing process.
This approach offers a balance between professional support and creative autonomy, appealing to authors who seek both expertise and independence.
Pros of Hybrid Publishing
Shared Expertise: Authors benefit from professional services, such as editing and design, provided by the hybrid publisher. This collaboration ensures a high-quality product while allowing authors to focus on writing.
Hybrid publishers often have experienced teams that guide authors through the publishing process, offering valuable insights and support.
Flexibility and Control: Authors maintain more control over the creative process compared to traditional publishing, with the support of industry professionals. This flexibility allows authors to retain their artistic vision while benefiting from expert advice. Authors can choose which services to pay for, tailoring the publishing package to their specific needs and budget.
Faster Publication: Hybrid publishing typically offers a quicker path to publication than traditional methods. This speed allows authors to bring their books to market in a timely manner, responding to reader demand and industry trends.
By streamlining the process, hybrid publishers enable authors to focus on promoting their work and engaging with their audience.
Cons of Hybrid Publishing
Cost: Authors often need to invest upfront, similar to self-publishing, which can be expensive. The costs associated with professional services can add up quickly, requiring authors to carefully budget and plan. While the investment can lead to a high-quality product, it may not be feasible for all authors.
Varied Quality: The quality of hybrid publishers can vary widely, so it’s crucial for authors to research and choose reputable companies. Not all hybrid publishers deliver on their promises, and some may lack the resources or expertise to provide meaningful support. Authors should vet potential partners thoroughly, seeking reviews and recommendations from other authors.
Complex Royalties: The royalty structure can be complex, often falling somewhere between traditional and self-publishing rates. Authors must navigate these agreements carefully to understand their earning potential and financial obligations.
Transparency in royalty agreements is essential to avoid unexpected surprises and ensure fair compensation for the author’s work.
Academic and Open-Access Publishing
For authors in academia, academic publishing and open-access publishing provide additional pathways. These methods focus on making research and scholarly works widely accessible.
Lambert Academic Publishing, for instance, specializes in publishing theses and academic projects with global reach.
Open-access publishing allows authors to share their work freely, increasing visibility among researchers and readers. However, authors often pay article processing charges (APCs) to support free access.
Recent stats show that the global Open Access Journal Publishing market is projected to reach $3.2 billion by 2028, emphasizing its expanding role in the academic publishing industry.
Free AI Tools for Promoting Your Work
Regardless of how you decide to publish your book, promoting it effectively is essential. Free AI tools for promoting your book, like ChatGPT for crafting marketing copy or Canva for designing social media posts, can save time and boost your outreach efforts.
Leverage these tools to build an audience and engage readers across platforms.
Conclusion
Choosing the right publishing model—traditional, self-publishing, or hybrid—depends on your creative goals, budget, and desired level of involvement in the publishing process. Each method has unique advantages and challenges, so consider your priorities carefully.
Whether you’re exploring academic publishing, open access, or tools to enhance your book’s visibility, success lies in understanding your audience and delivering a compelling product.
By staying informed and using the right strategies, following publishing trends, you can bring your work to life and ensure it reaches the readers it deserves.
